Is MB a safe alternative to allopurinol?
Methylene Blue (MB) is not a replacement for allopurinol in managing gout or high uric acid levels. Allopurinol is a well-established medication used to lower uric acid levels by inhibiting the enzyme xanthine oxidase, which is responsible for the production of uric acid. On the other hand, Methylene Blue (MB) works through different mechanisms, primarily related to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Understanding Allopurinol vs. Methylene Blue
Allopurinol is a drug specifically designed to lower uric acid levels and prevent gout flare-ups. It is widely used for managing chronic gout and hyperuricemia
Methylene Blue (MB), while beneficial for antioxidant support and mitochondrial function, does not directly affect uric acid production.
Instead, it might support general joint health and reduce inflammation, which could complement traditional treatments
Why MB Is Not a Direct Alternative to Allopurinol
Different Mechanisms
Allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase, which directly lowers uric acid levels, making it effective for managing gout.
MB does not have a direct effect on uric acid production. While it can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, it does not treat the root cause of gout—elevated uric acid.
Lack of Evidence
While MB has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, there is no clinical evidence to support that it can lower uric acid levels or prevent gout attacks in the way allopurinol does
Different Therapeutic Roles
MB might serve as a complementary supplement for reducing inflammation and improving cellular health, but it is not a first-line treatment for gout management
Who Should Consider MB for Gout?
Individuals with Gout Flare-ups: MB may help manage inflammation during a flare-up due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, but it should not replace allopurinol or other uric acid-lowering medications
People Seeking Joint Support: MB might be useful for individuals looking to support joint health or reduce chronic inflammation in a broader context, though this is more of a preventive approach
Final Thoughts
While Methylene Blue has some promising anti-inflammatory effects that may support overall joint health, it is not a effective substitute for allopurinol in treating gout or managing uric acid levels. Allopurinol remains the primary treatment for lowering uric acid and preventing gout attacks, while MB may serve as a complementary support to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
3 FAQs
Q1: Can I use MB with allopurinol?
A: Yes, MB might complement allopurinol by reducing inflammation, but it should not replace it. Always consult a doctor before combining treatments.
Q2: Can MB help during a gout flare-up?
A: MB may help alleviate inflammation and oxidative stress during a flare-up, but it won’t lower uric acid or prevent future attacks.
Q3: Is MB safe to use alongside prescription medications?
A: In general, MB is safe when used at appropriate doses. However, consult a doctor before using it alongside prescription medications like allopurinol.
Sources:
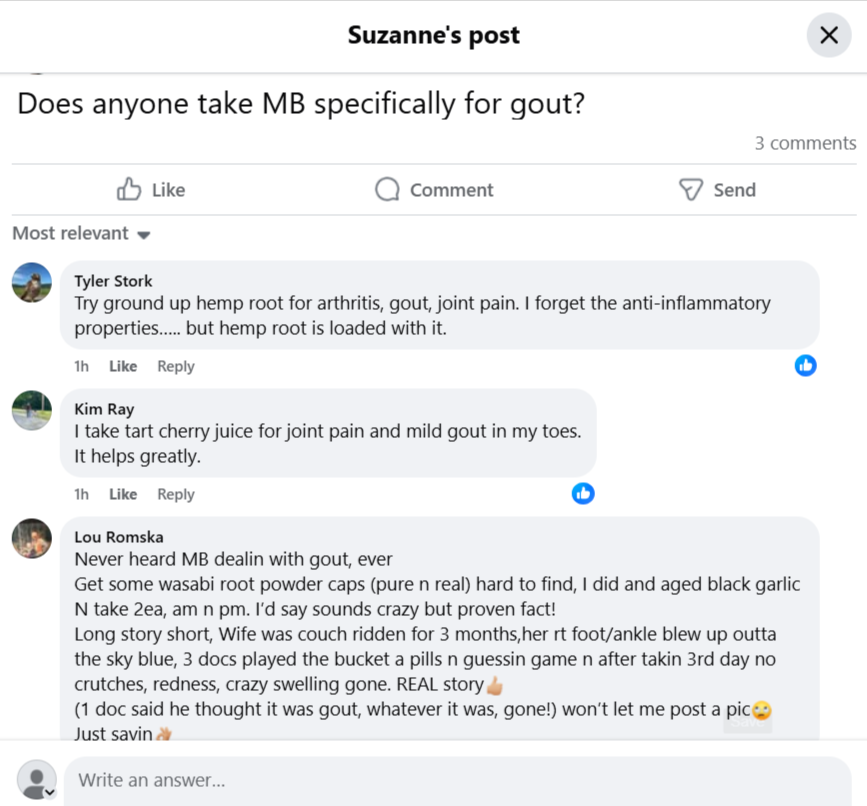
Some comments from users:
Topic Participants
Karl P
Sticky Posts
Which brand of Methylene Blue should I purchase?
Background We receive product photos from members asking if the brand is reliable/safe. Unfortunately, there has been a rise in dubious MB brands of late - so we have tried to prepare a checklist to assist. It is not comprehensive, but it's a guide. WhenWhat is the recommended Methylene Blue Dosage to improve memory & for Anti Aging?
Background There are multiple different dosages that are discussed as suitable dosages to be used - this confuses people. The reason for multiple doses is because : It is a 120 year old drug and at different times it was used for different purposes at